Image Contrast Examples#
This page shows examples of different MRI contrasts, as well as examples of how to simulate MRI contrast.
Learning Goals#
Describe how various types of MRI contrast are created
Identify various image contrasts
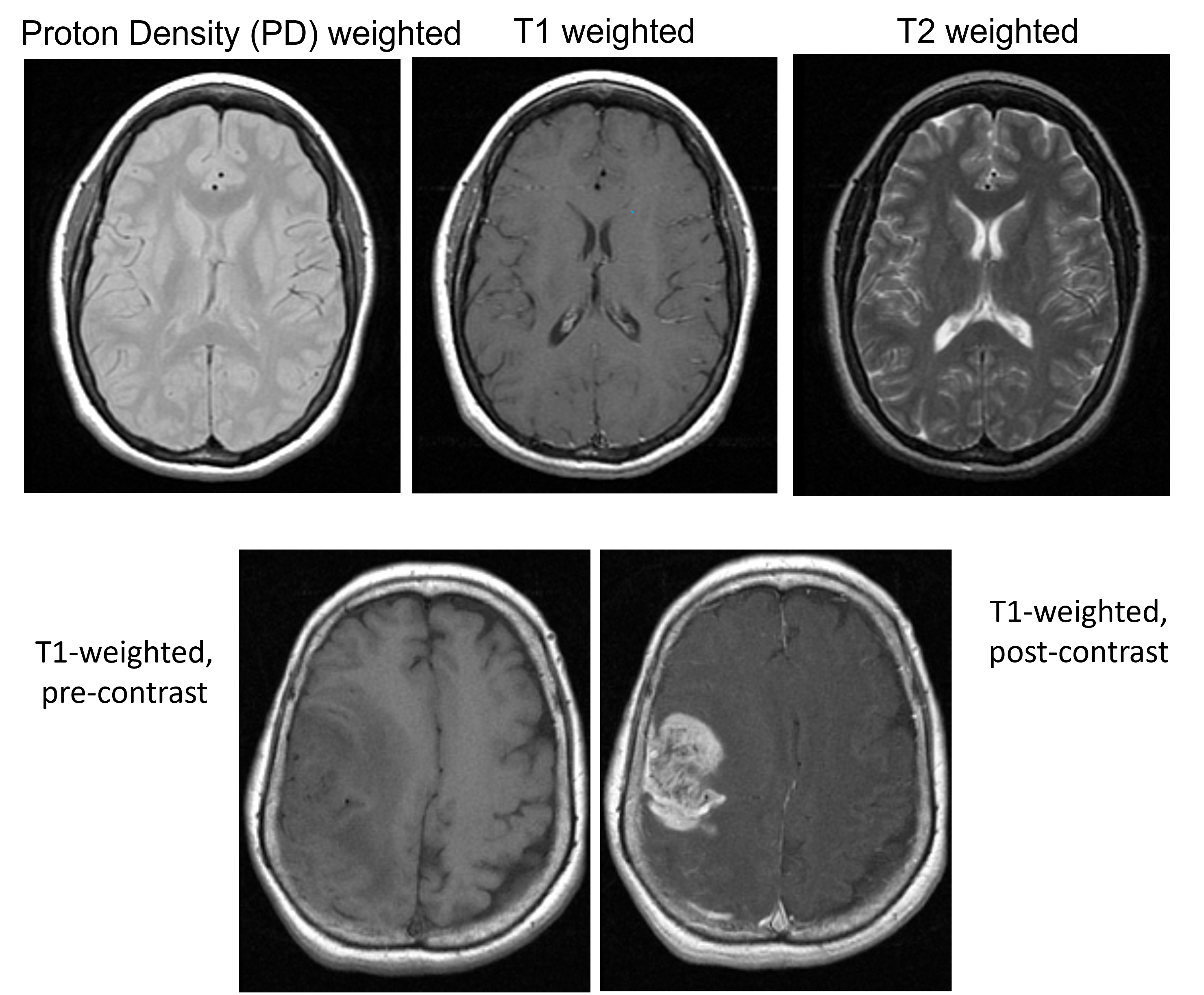
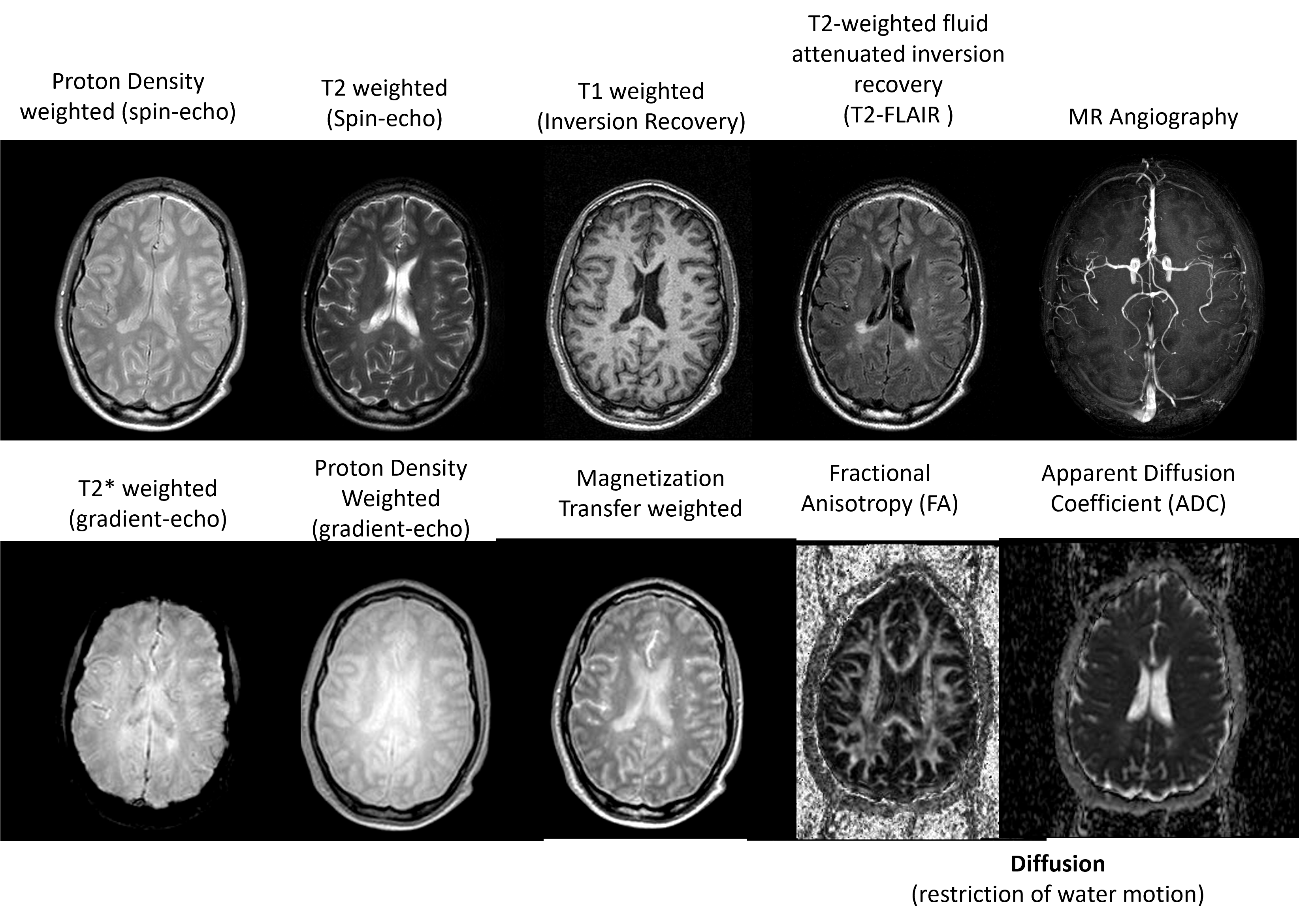
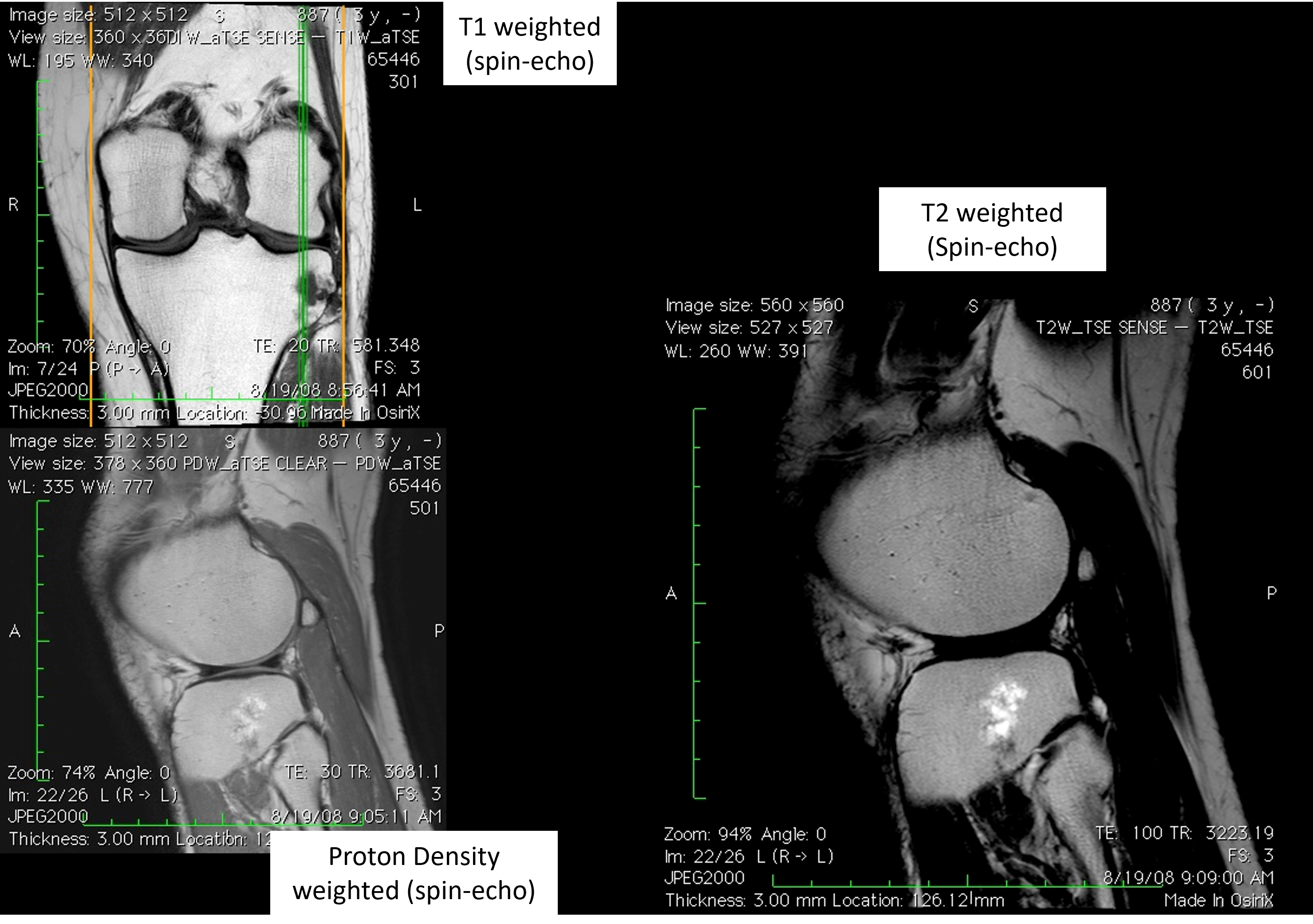
Image Contrast Examples#
Simple Contrast Phantom#
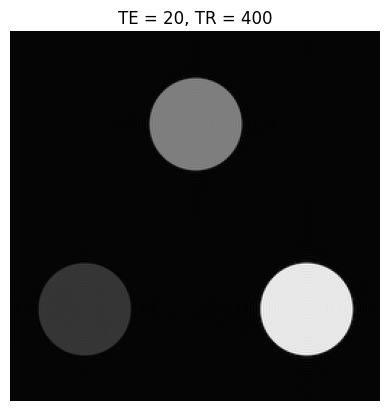
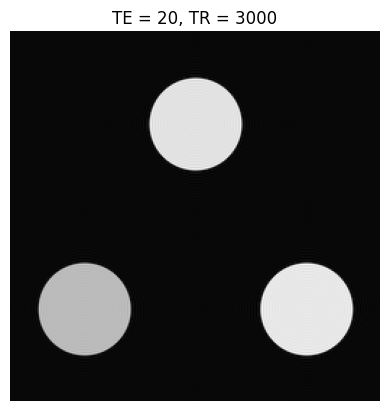
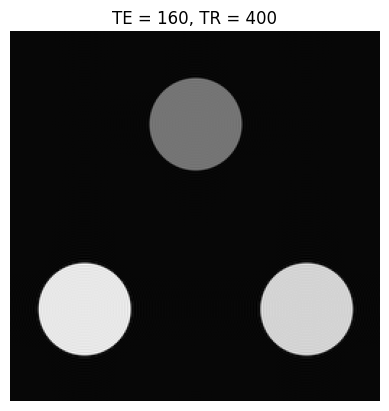
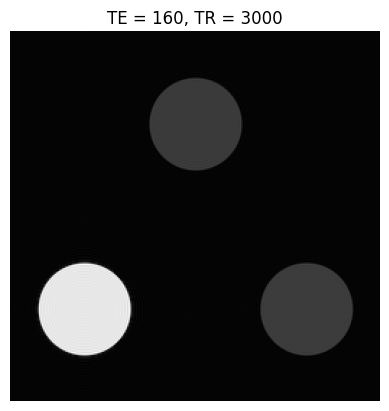
Below is a simple contrast phantom consisting of three circular objects, each with a different \(T_1\) and \(T_2\). The k-space data for these phantoms is created using a “jinc” function, which is the Fourier Transform of a circle:
\[\mathcal{F}\{ \mathrm{circ}(r) \} = \mathrm{jinc}(k_r)\]
The signal is simulated for varying sequence parameters (TE, TR) with a 90-degree flip angle in a gradient-echo scheme by using the helper function:
signal_gre = MRsignal_spoiled_gradient_echo(flip, TE, TR, M0, T1, T2)
Challenge Yourself!#
Based on the images and TE/TR parameters below, can you estimate T1 and T2 relaxation times of the 3 objects?
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.special import j1
# Helper functions (you must define these elsewhere in your notebook or import them)
def jinc(x):
# Avoid division by zero
result = np.ones_like(x)
mask = x != 0
result[mask] = j1(np.pi * x[mask]) / (2 * x[mask])
return result
def MRsignal_spoiled_gradient_echo(flip, TE, TR, M0, T1, T2):
# Calculate the MR signal for a spoiled gradient echo sequence
E1 = np.exp(-TR / T1)
E2 = np.exp(-TE / T2)
return M0 * (1 - E1) * np.sin(flip) * E2 / (1 - E1 * np.cos(flip))
Nphan = 3
# phantom parameters
xc = np.array([-.3, 0, .3]) * 256 # x centers
yc = np.array([-.25, .25, -.25]) * 256 # y centers
M0 = np.array([1, 1, 1]) # relative proton densities
T1 = np.array([.3, .8, 3]) * 1e3 # T1 relaxation times (ms)
T2 = np.array([.06, .06, .2]) * 1e3 # T2 relaxation times (ms)
r = 1/64 # ball radius, where FOV = 1
flip = 90 * np.pi / 180
TEs = [20, 160]
TRs = [400, 3000]
N = 256
# matrices with kx, ky coordinates
kx, ky = np.meshgrid(np.arange(-N/2, N/2) / N, np.arange(-N/2, N/2) / N)
for TE in TEs:
for TR in TRs:
# initialize k-space data matrix
M = np.zeros((N, N), dtype=complex)
# Generate k-space data by adding together k-space data for each individual phantom
for n in range(Nphan):
# Generates data using Fourier Transform of a circle (jinc) multiplied by complex exponential to shift center location
M = M + jinc(np.sqrt(kx**2 + ky**2) / r) * \
np.exp(1j * 2 * np.pi * (kx * xc[n] + ky * yc[n])) * \
MRsignal_spoiled_gradient_echo(flip, TE, TR, M0[n], T1[n], T2[n])
# reconstruct and display ideal image
m = np.fft.fftshift(np.fft.ifft2(np.fft.ifftshift(M)))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(np.abs(m), cmap='gray', aspect='equal')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(f'TE = {TE}, TR = {TR}')
plt.show()